Inside the Issue, Spring 2025
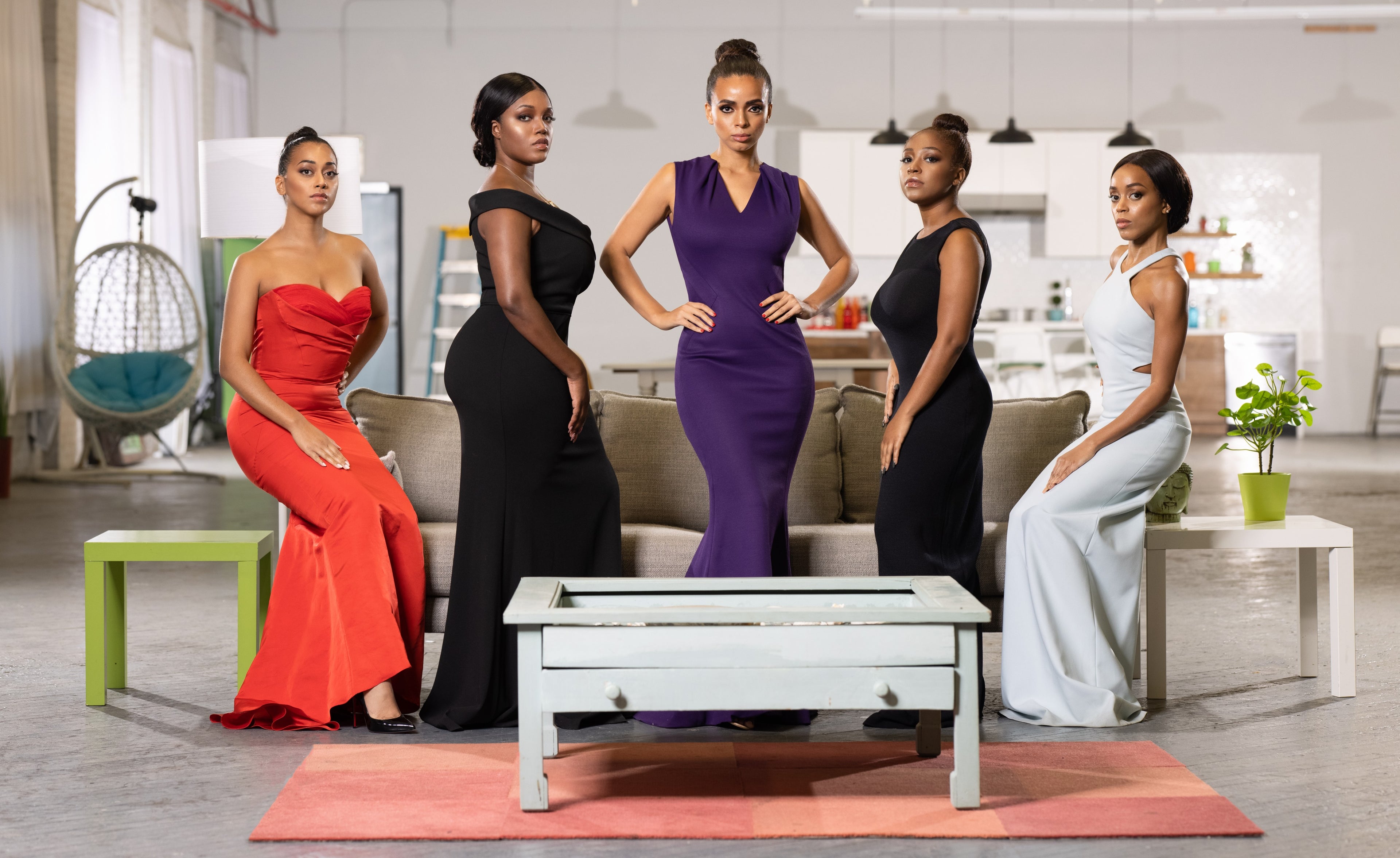
She's SINGLE Magazine is now the foremost source for prestigious relationship advice, offering insights tailored to strong, independent women who are redefining love on their own terms. As a go-to relationships magazine for modern, ambitious women, She’s SINGLE shifts the narrative from "waiting for the one" to thriving while single, empowering readers with advice on self-care, personal growth, and building a life they love.

There are two ways to attend The Manhattan Dinner: You can apply to purchase tickets for $1,499.00, which includes two raffle tickets. If selected, your application fee will be deducted from the ticket amount. Alternatively, Elite Missies and Matchmaker Couples can use their SUBcode to purchase tickets at 50% off and receive four raffle tickets.
PRINT STORIES.
WHY DO MEN LOVE THE CHASE BUT LOSE INTEREST AFTER?
DOES HE SEE YOU AS WIFE MATERIAL? HERE’S HOW TO KNOW
WHY YOU MISS SEX WITH YOUR EX
HOW TO MAINTAIN FRIENDSHIPS IN DIFFERENT LIFE STAGES

When the time is right, subscribers can take the next step by connecting with eligible bachelors and, if they’ve found their perfect match, attending The Exclusive Manhattan Dinner, an invite-only event held on the first Monday of October, where select couples and singles gather for a night of luxury, connection, and celebration.
YOUTUBE.

REIGN: Power, Passion & The Women Who Run It All
Celebrate the triumphs of global entertainer and entrepreneur Beyoncé Giselle Knowles in this special edition of She’s SINGLE Magazine. Following her historic AOTY win at the 67th Grammys, Beyoncé cements her place in history as the fourth Black woman to achieve this honor, after Natalie Cole, Lauryn Hill, and Whitney Houston.
This exclusive Spring 2025 issue is a tribute to women who dominate in their fields, from luxury handbag designers to premium women-owned wine companies.
DIGITAL NEWSSTAND.
-
REIGN: Power, Passion & The Women Who Run It All (Digital Spring 2025)
Regular price $14.88Regular priceUnit price per -
Melanin In Motion (Winter 2025)
Regular price $8.88Regular priceUnit price per -
LGBTQ+ Love Stories (Fall 2024)
Regular price $8.88Regular priceUnit price per -
The Love Lounge Issue (Spring/Summer 2024)
Regular price $8.88Regular priceUnit price per